London Under Danish Rule: Cnut’s Politics and Policies as a Demonstration of Power
In 1016, London was one of very few English cities of European significance. This reflected London’s prominence as a trading port, an economic and administrative hub, and population centre, rather than any status as a nascent capital city.
Failed engineering project doomed medieval Cambodian capital, study finds
The largest water management feature in Khmer history was built in the 10th century as part of a short-lived medieval capital in northern Cambodia to store water but the system failed in its first year of operation, possibly leading to the return of the capital to Angkor.
Crusader Urban Archaeology in the Kingdom of Jerusalem: Methodologies, Constraints and Possibilities: The Cases of Jerusalem and Acre
I might have called this paper a Tale of Two Cities for that certainly what it is – a tale of two very different cities and how they contribute to our understanding of the Crusader period and the Latin East
How Coal Played a Part in Medieval Air Pollution
Pollution was a problem long before the Industrial Revolution and complaints of air pollution and its association with fuel can be traced back over seven hundred years.
Around the Barbarian Sea: Settlements and Outcomes in the Early Medieval Baltic
The Viking towns of Birka, Kaupang, Hedeby and Ribe have captured the imagination of archaeologists and the public alike, presenting the lives of their enigmatic inhabitants.
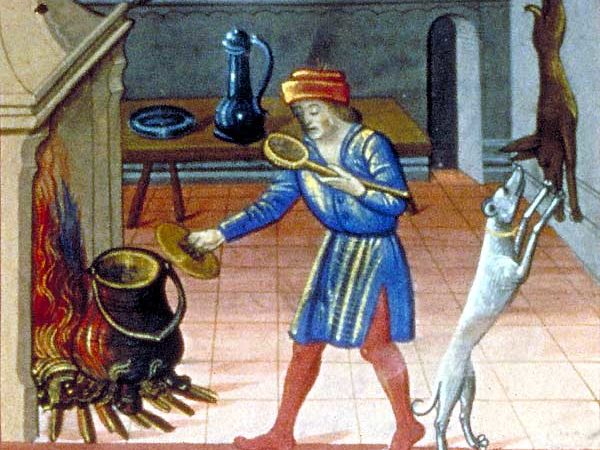
The Medieval English Urban Cook
It utilises civic records, wills and probate inventories, literary sources, and archaeological evidence with the goal of building context which can inform the future study of medieval urban cooks.
Economic Power in Rome. The role of the city’s elite families (the 1400-1500 period)
In this paper we examine a less explored area, namely the existing relationship between political stability and the economic success of the merchant elite
Prostitution in Urban Brothels in Late Medieval Austria
Municipal authorities officially established urban brothels in late medieval Austria as a necessary evil in order to control the lust of unmarried men and thus protect women from sexual abuse
Call for Papers: Provisioning Medieval European Towns
This year, from October 10th to the 12th, the Institute for Medieval Studies (IEM | NOVA-FCSH) and the Portuguese municipality of Castelo de Vide are organizing the IV International Conference on the Middle Ages, under the theme: Provisioning Medieval European Towns.
A Fruitful Partnership: Jews and the Canons of St. Kilian in Twelfth-century Würzburg
Over the course of about a century, from around 1120 to around 1220, the canons of St. Kilian, caretakers of the Neumünster church in Würzburg had frequent – one might even say constant – business dealings with the Jews of that same city.
The ‘Van Boschuysen Affair’ in Leyden: Conflicts between Elite Networks in Late Medieval Holland
The 1480s were a turbulent age in the city of Leyden in the county of Holland.
An Invisible Landscape of Medieval Rome
I look to the period when the monastery was assembling its real estate portfolio to analyze how property documents inform us about the origins of this urban region, its social networks and its physical development.
City notaries and the administration of a territory: Lucca, 1430–1501
The present article examines the functions, personnel, reputation and effectiveness of notaries in the service of fifteenth-century Lucca following the restoration of liberty.
Waste Management and Attitudes Towards Cleanliness in Medieval Central Europe
The paper deals with the relationships between people and waste in the Middle Ages, primarily in urban environments in Central Europe.
Nuremberg’s Noble Servant: Werner von Parsberg (d. 1455) between Town and Nobility in Late Medieval Germany
Through this appreciation of the factors supporting town–noble cooperation in the late Middle Ages we are better able to understand the formation and development of the dialectic of town and nobility as a way of understanding German society.
The economy of Norwegian towns c. 1250-1350
The aim of this thesis is to explain why differences arose between Norwegian, Danish and English towns with regard to their economic functions
Wild animals and medieval towns
In the year 1166, the town of Carmarthen in southern Wales was attacked by a rabid wolf, which bit 22 people.
Walking in Sixteenth-Century Venice: Mobilizing the Early Modern City
By studying physical motion, we can capture the dynamism of early modern cities and, drawing on all the rich meanings of the Italian verb movimentare, move, mobilize, invigorate, and enliven the history of early modern urban society and culture.
Krakow, the Old Town – A Continental Venice
Surviving the destructions of the war, the old town of Krakow is a lesson of architecture and urbanism through the multitude of architectural styles, coherence and urban continuity.
Mensuration in Early Medieval Barcelona
Various units of length are found in use in early medieval Barcelona, but the dexter is by far the most common. However, the interpretation of its value is by no means straightforward.
Decline or Transformation? Archaeology and the Late Medieval ‘Urban Decline’ in Southern England
Decline or Transformation? Archaeology and the Late Medieval ‘Urban Decline’ in Southern England By Ben Jervis Archaeological Journal, Vol.174:1 (2017) Abstract: Archaeological evidence is…
Constraining Elites: The Self-Enforcing Constitution of the Patricians of Venice
This paper analyzes how late Middle Age and Renaissance era Venice achieved economic prosperity despite being ruled by elite patricians.
Death of a Renaissance Record-Keeper: The Murder of Tomasso da Tortona in Ferrara, 1385
Beginning with a description of the murder of an Italian record-keeper at the hands of an angry mob in the late fourteenth century, this essay explores the historical background of official records destruction during the Renaissance
A millennium of Belgrade (Sixth-Sixteenth centuries): A Short Overview
This paper gives an overview of the history of Belgrade from the reign of Justinian I (527–565), i.e. the time of Slavic settlement, to the Ottoman conquest in 1521.
Changing Places: a comparative discussion of London and Tours in the Early Medieval Period
This paper examines the developmental stages that occurred at two settlements which saw significant changes from the 5th to 12th centuries AD; London and Tours.